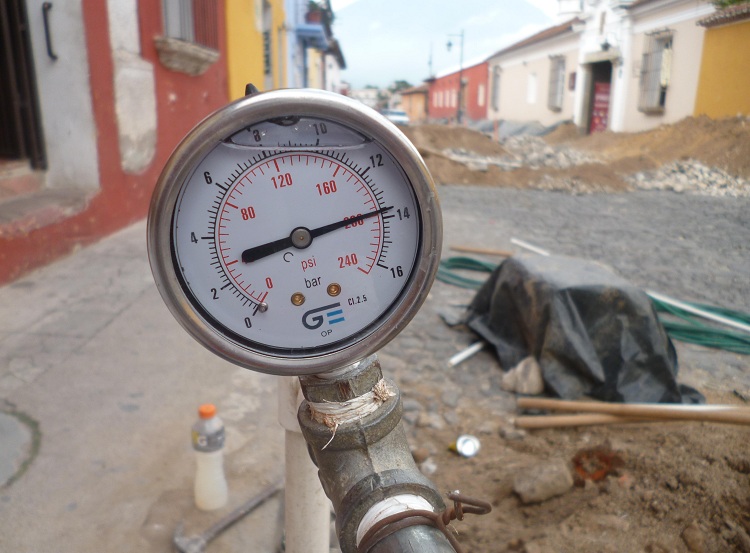
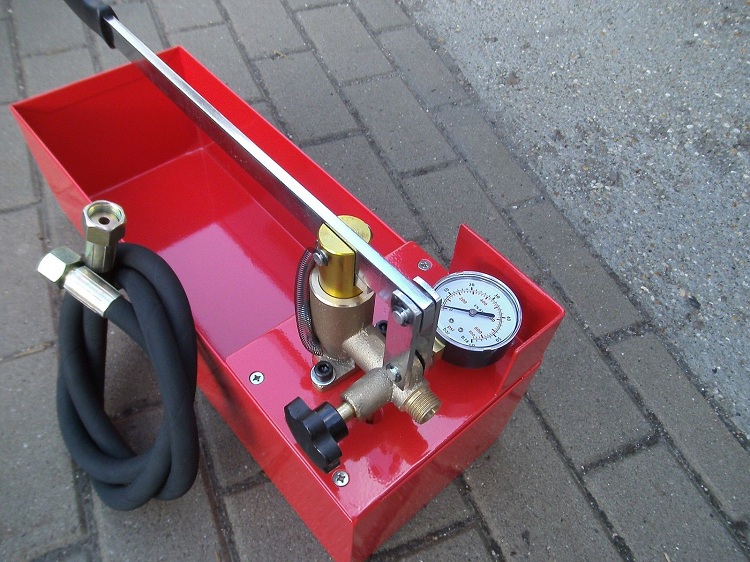
Pipeline crimping is a process operation performed on a relatively small isolated section of the pipeline. This section is a special test by applying high pressure, close in value to the maximum allowable. Pressure testing of pipelines allows you to verify the integrity of the line, the quality of installation work and installation of fittings.
Content
The concept of crimping pipes
Crimping is understood as checking the readiness of an object for operation by applying high pressure. The object of such a check can be a pipeline system, a tank, an aggregate or a machine, a separate mechanism. Speaking of elevated pressure, they mean a value that is 2-3 times higher than the working one and approaches the maximum permissible value. An object that has successfully passed crimping is considered suitable for work. The places where leaks were detected during the inspection are repaired.
Important! The pressure during crimping is regulated by regulatory documents for certain groups of objects.
Crimping should be done by a trained specialist. Relevant employees of industrial and communal enterprises are required to pass certification. At the end of the test, an act is signed in which the date, pressure value, holding time and other information are indicated.
The pressure in the system for testing is created either by a regular pump or by a special pressure tester. Check, as usual, with water. When its use, for any reason, is unacceptable, air pressure testing of the pipes is carried out, which makes it difficult to detect leaks.
When do pressure tests of pipelines
Before putting into operation, all new piping systems, tanks, etc. are subjected to pressure testing. All objects that have undergone repair or replacement of an element are also checked. Since it is customary to consider joints with installed fittings to be the most unreliable sections of the pipeline, the areas where the coupling was used to be coupled are mandatory to be checked.
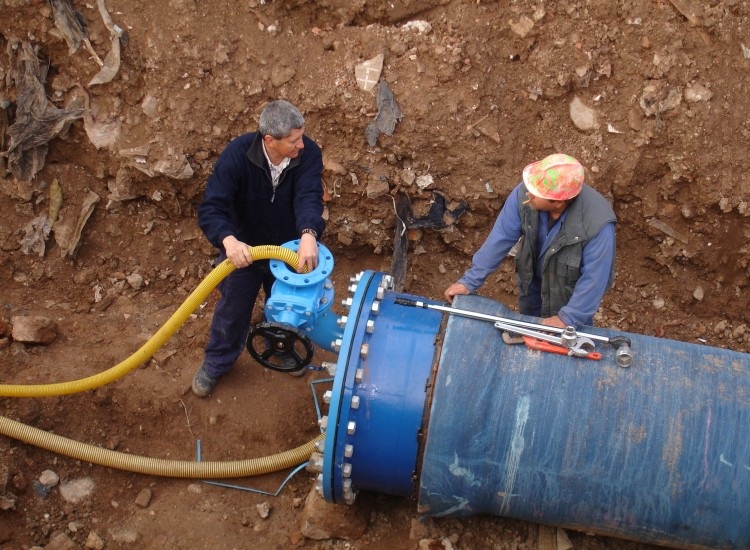

All types of pipelines, household and industrial, newly built and already operated, are subject to pressure testing.
A test is also carried out in other cases:
- if the pipeline has been idle for a long time or works in a seasonal mode (like a heating system in summer);
- if scheduled inspections are provided. Thus, the polymer sewage is checked when the integrity of the discharge pipe is controlled. Pressure test of a plastic water pipe belongs to one of the most popular operations carried out after any pipe cleaning, since mechanical damage is very likely, especially at the joints;
- after flushing the pipeline, especially with the use of aggressive chemicals, under the influence of which damage to the fittings or pipe walls could occur;
- Well testing is carried out in a special way - to check for the penetration of the top water (water from the surface layers) into its trunk, because consumers are concerned about the quality of water, especially drinking water.
Preparation for work
Crimping is a responsible procedure that requires preparatory measures. Before testing the pipeline, without fail:
- An inspection is carried out in order to identify visually detectable defects (rusted areas, the absence of any parts, etc.). If violations are identified, they are eliminated. In cases where the system contains a working medium that is forbidden to be used for testing, it is customary to release it (for example, the heating system is freed from the coolant).
- The pipes are flushed to remove rust, scale, and deposits of organic and inorganic origin from them. Some of the flushing methods require a compressor. Upon completion of washing, the quality of its performance is checked. The quality of washing is checked by the condition of the inner surface of a half-meter section of the pipeline cut out at an arbitrarily selected location.
If the discharge device does not have a non-return valve holding the working medium in the system and a pressure gauge, then they are installed after the tests are completed.
It's important to know! Pressure testing of the heating system of an apartment building precedes the verification of work on the preparation of the associated thermal unit. This is due to the fact that the thermal unit is checked using large pressure values.
Mechanisms for
Criminists, i.e. special pumps for the relevant tests differ in design. On this basis, they are classified into three types:
- Piston.
- Lamellar-rotary.
- Membrane.
If you need to test a pipeline (or other facility) of a relatively small volume (for example, in private housing construction), then it can be performed using an inexpensive and easy-to-use manual crimping tool. Such a mechanism allows up to three liters of working fluid to be pumped into the system in a minute.
To check the systems of a multi-storey building, you will need a more powerful mechanism driven by an internal combustion engine or electric. The domestic UGO-30 is equipped with a 16-liter tank and allows you to develop a pressure of up to 30 atm. Manual two-stage pumps UGO-50 and UGO-450 are used for more complex tasks.
German-made crimping machines manufactured by Rothenberger (model ROTEST GW 150/4, for example, designed for air testing of drinking water and gas supply systems) and Ridgid (for example, model 1460-E 19021 are used in systems filled in as a working fluid with water, oil or ethylene glycol).
SNiP and safety measures during crimping
The procedure for testing pipelines, technological schemes of the crimping process and safety standards are determined by the relevant sections of SNiP:
- for internal sanitary systems - SNiP 3.05.01-85;
- for external drainage systems - SNiP 3.05.04-85;
- for heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems - SNiP 41-01-2003.
Industry regulatory documents determine the procedure for crimping on industrial pipelines.
The specified documents establish the value of the pressure allowed during the test. This value is determined by the material of the pipes, the minimum thickness of their walls, the difference in height between the lower and upper elements of the tested system and other factors. During hydraulic and pneumatic tests, the pressure value can be (in atm):
- for pressure pipelines of water supply systems - 10-15;
- for cast iron sewer - 1.5;
- for non-pressure polymer pipelines - 1.5 - 2;
- for heating systems of apartment buildings where cast-iron radiators are installed - 2-5 (but not less than a value exceeding the working pressure by 1.5 times);
- for input nodes of centralized systems - 10;
- for private houses - 2 (since the emergency valve is usually set to this level).
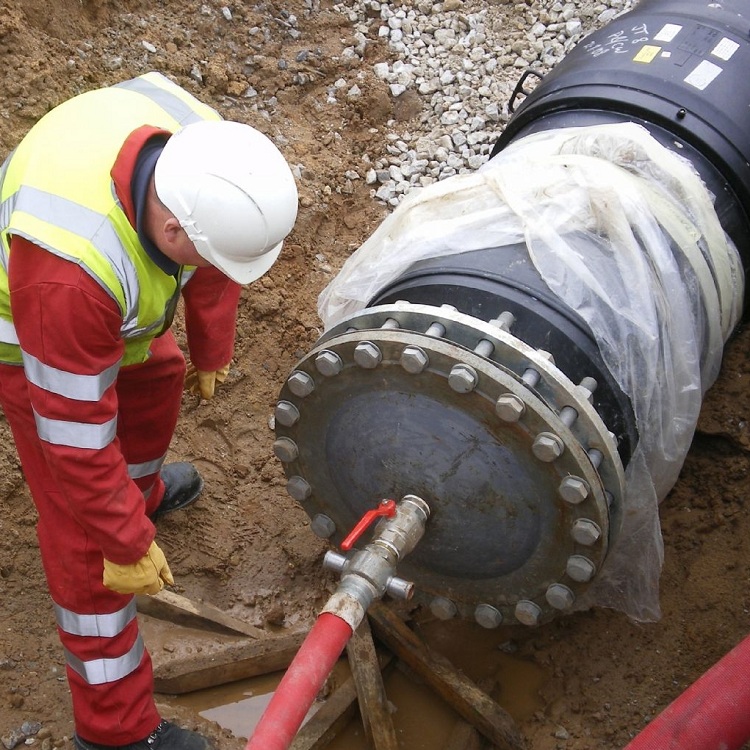

Pressure testing should be carried out in accordance with SNiP, taking into account the type of line and the material of pipes installed in it
Important! During testing, the main requirement for compliance with safety measures is to follow the recommended pressure limit. To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is recommended to use a crimper equipped with a special limiter during testing.
General procedure for conducting pneumatic and hydraulic tests
The test setup for air and water is general. The procedure is as follows:
- Within the test object, a part of it is isolated by means of shut-off (adjusting) fittings (sewer pipes are closed with rubber plugs or wooden corks wrapped in rags).
- The test object is filled with water. When testing heating systems when filling with water, air is discharged through special air vents in the upper part.
- The crimp is connected to the system, pumping a certain amount of working fluid to create the pressure required by the regulatory standards.
- Having reached the required pressure value recorded by the observer on the manometer, the crimping tool is turned off.
- The system is left under pressure for a certain time (for heating systems - at least half an hour; in some cases, the exposure time can be 6-8 hours).
- At the end of the assigned holding time, the observer again reads the pressure gauge. The difference in gauge performance is evidence of a leak in the system that needs to be detected and repaired.
Note! After eliminating the leak, pressure testing is carried out again.
Pressure testing of pipelines with air and water
To conduct a test of the operability of a heating system, water supply or sewage system, a pump (special or circulating fluid in the system) will be required. It connects to the heating system either:
- directly to a tap designed to drain the working fluid from the heating system;
- to any of the radiators. To do this, the Mayevsky crane is removed, and an adapter is installed in its place, to which the hose from the compressor is connected.
The test of the water supply system is carried out through the connection pipe of the taps, through which cold or hot water is supplied. To connect to the sewage system, it will be necessary to insert the sediment fitting into one of the revisions, special tees mounted in the outlet pipe every 40-50 m.
Buying a crimper for personal use, which will be used once a year, is hardly advisable. Which pump to use for pumping air or water into the system is determined based on the amount of pressure that needs to be created for the test (and it should exceed the working one by 2-3 times). To pressure test the heating system of a private home, an automobile compressor or an electric pump should be enough.