Effective heating systems for a single-story or multi-story building can be organized with forced or natural circulation, according to a one-pipe or two-pipe principle. The most common is the second option. A number of convincing and important factors determine the feasibility and relevance of using a two-pipe heating system. In addition, work can be done with your own hands.
Content
- 1 The device of two-pipe heating systems
- 2 Elements of a heating system
- 3 Horizontal and vertical systems
- 4 Wiring a two-pipe heating network
- 5 Features of the application of the upper and lower wiring
- 6 Properties of forced and natural circulation
- 7 Features of heating a one-story and two-story building
- 8 Installation Rules
The device of two-pipe heating systems
A design feature of the two-pipe wiring of heating is the presence of a supply and return line. The coolant is heated in the boiler, and then transported and distributed along one of the pipelines through registers and devices. Another takes and returns the cooled liquid back to the heat generator.
Note! The two-pipe heating system of a private house (or multi-storey building) provides heat to all heating devices with the same temperature. In a one-pipe scheme, heated water sequentially passes through a chain of radiators and pipes, losing heating characteristics when approaching the last of them.
Water in such a system can be supplied directly from the water supply. An expansion tank is needed for it. It happens with water circulation or simple. The structure of the latter includes a tank and 2 pipes: one of them is a riser supplying water, the other to drain excess fluid.
Two-pipe heating systems of a single-story house (or multi-storey) can operate using a pump to provide forced circulation.
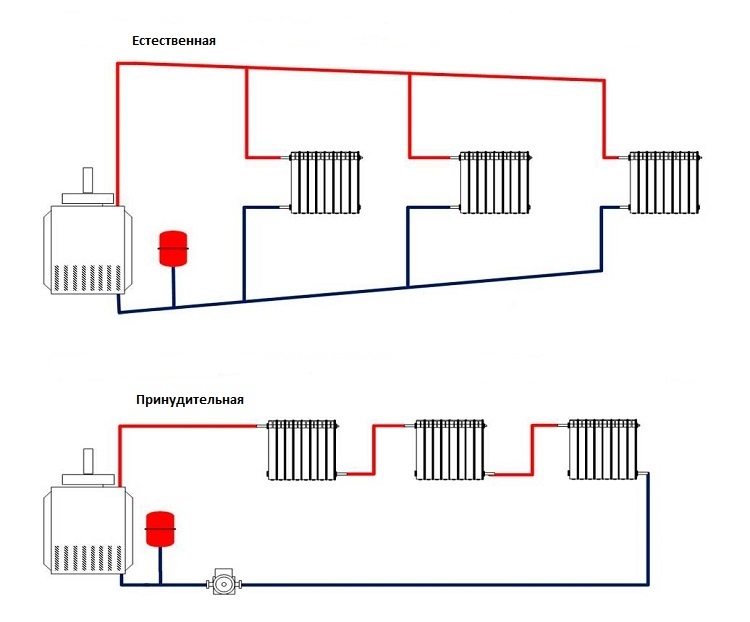
The heating scheme with forced circulation of the working fluid involves the installation of a special pump in the immediate vicinity of the boiler
In practice, standoffs and elements with a by-pass flow (direct-flow) are distinguished. In the first method, the movement of heated water is opposite to the direction of the cooled. In the second case, the directions of movement of the return and direct coolant coincide.
Elements of a heating system
The layout of the two-pipe heating system of a private house implies the presence of such materials:
- a boiler (or other means for heating water);
- safety valve;
- expansion tank;
- reagents for cleaning;
- pump (associated with water circulation);
- radiators;
- air venting mechanism;
- pressure gauge (determines pressure);
- additional fittings;
- pipes.
To install a two-pipe heating system in a private house, various tools may be required: a hammer, a welding machine, a drill, a gas and adjustable wrench, a tape measure, a plumb line and a level, a screwdriver.
Two pipes are mounted in all radiators, cranes are installed in front of each of them, with the help of which any heating element can be disconnected from the heat transfer if necessary.
From the boiler (or from the furnace), the main pipe goes up, which delivers the hot coolant.It is connected to a compensating tank having a drain and a signal pipe.
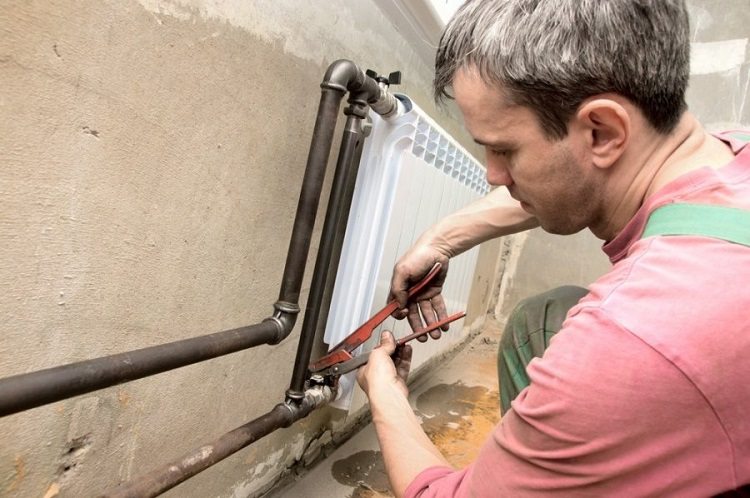

To each heating radiator in the house two pipes are connected, equipped with taps to turn off the heat supply
A pipeline is drawn from the tank to the upper line, from which the communications are routed to all radiators included in the system. A pump is mounted at the outlet or at the inlet of the boiler unit with a two-pipe heating system with forced circulation. The return line is drawn parallel to the laid highway, connected to radiators, fed and cut into the lower part of the boiler.
Thermal energy consumption is controlled by thermostats.
Horizontal and vertical systems
The division of the heating system into vertical and horizontal determines the placement of pipes that connect all the appliances into a single whole.
Note! Both types of heating circuits are characterized by excellent hydraulic and thermal stability.
A two-pipe horizontal heating system is more characteristic of a one-story building, which has a considerable length. In such buildings, it is more reasonable to connect radiators to a pipeline laid horizontally. This method of organizing heating is convenient for panel-frame buildings, housing, where wiring is performed from risers located in the corridor or on the stairwell.
Two-pipe heating systems of multi-storey buildings of predominantly vertical type. Such an organization is more expensive, but air traffic jams will not interfere with efficient operation. All devices in this case are connected to a vertical riser, and each floor is connected separately.
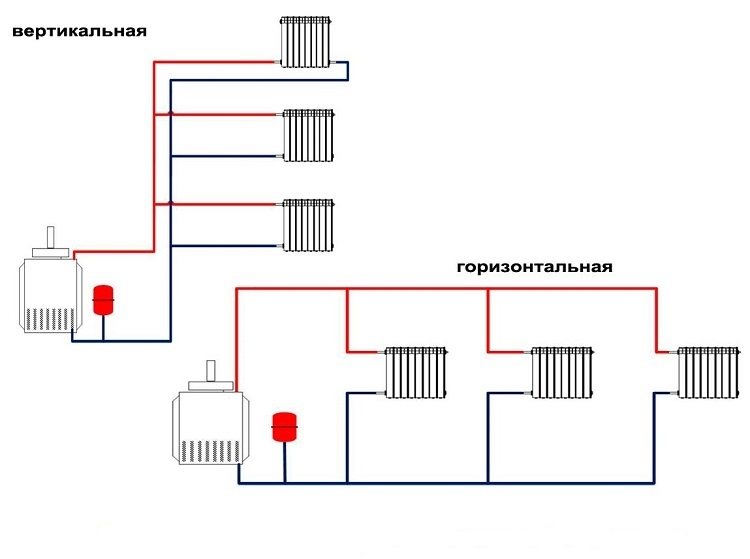
If the house is multi-story, you need to apply a vertical diagram of the heating system, and in a one-story building, the horizontal option is optimal
Wiring a two-pipe heating network
According to the method of construction, heating system circuits are divided into networks with upper and lower wiring.
The method with the lower wiring involves laying a highway with hot water in the underground space, basement or basement. The pipeline returning the cooled water back to the boiler is even lower. With lower wiring, the inclusion of an upper line in the circuit, which is responsible for the removal of excess air from the system, is required.
To ensure uniform transportation of heat to all devices, the boiler must be buried, and the batteries were located above it.
The upper wiring is characterized by the upper laying of the distribution pipe. The expansion tank is then installed at the highest point of the heating circuit. Usually it is located in a heated attic. Thus, for a one-story house with a flat roof, the scheme of a two-pipe heating system with an upper wiring is not suitable.
Features of the application of the upper and lower wiring
Both types of wiring are applicable for horizontal or vertical do-it-yourself organization of two-pipe heating of a private house (single or multi-story).
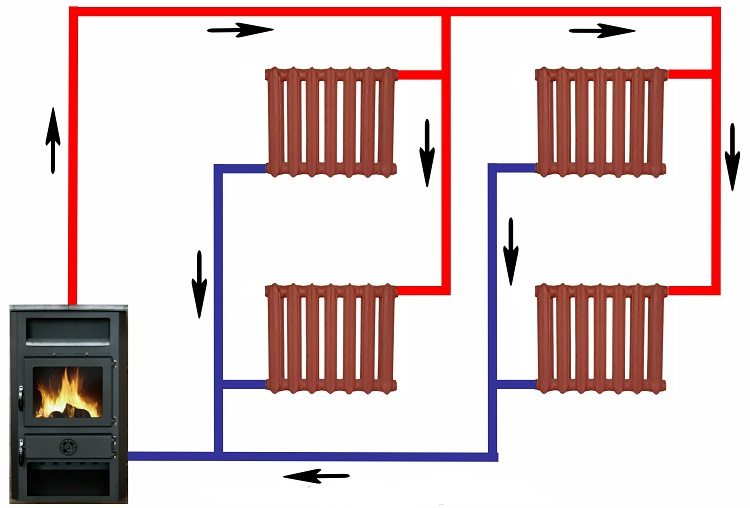
Both the lower and upper wiring have their own subtleties, and in order to avoid mistakes, you need to carefully study the circuit of both of these systems
For multi-storey buildings, which are of the vertical type, the installation of a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring is more characteristic. This is due to too much pressure created by the difference in processing temperatures and heated coolant, which increases with the next floor.
Note! The additional pressure at the lower wiring helps the coolant to move through the pipeline. If it is impossible for structural reasons to perform the lower wiring, the construction of the upper supply line is performed.
A pump can be introduced into the network with natural circulation at any time, the start of which will allow to warm up the room evenly and quickly if necessary.
Properties of forced and natural circulation
There are two-pipe systems with natural as well as forced circulation of the working fluid. With natural - the heat carrier expands from heating in the boiler, creates pressure in the network and moves along the circuit, gradually cooling in existing radiators. Such heating does not need electricity for proper functioning. For two-pipe heating systems with natural circulation, the correct execution of the angles of the communication slopes during installation and the accurate selection of pipe sizes are important.
The total length of the circuit should not be more than 30 meters. Natural circulation networks are used for small boilers and small houses. The efficiency of this method of heating the premises is lower than systems with forced circulation.
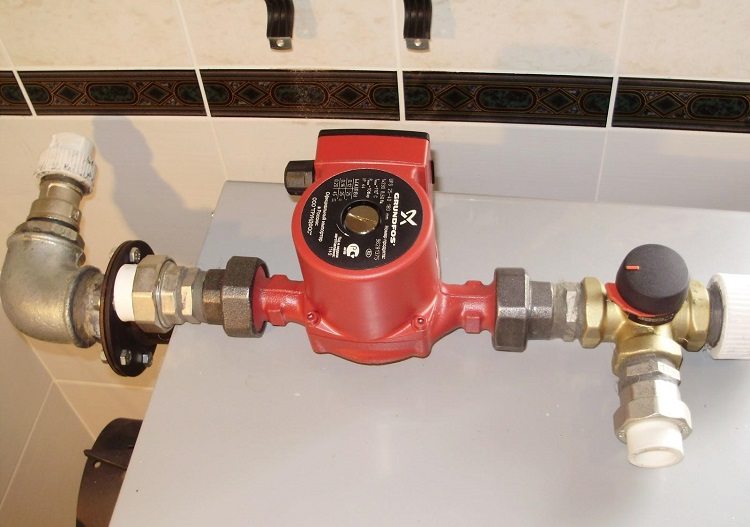

The circulation pump accelerates the movement of the coolant through the system and contributes to its uniform distribution over all heating devices (radiators)
A forced circulation network requires a circulation pump mounted in the pipe of the return branch. Such an installation eliminates its contact with a high-temperature coolant and extends its service life. Multiple pumps or one unit may be used. It all depends on the size of the house, the number and length of the wiring circuits.
The forced circulation system is characterized by independence from the temperature regime of the coolant, an increase in the length of the circuits, a variety of circuit design solutions for heating, the ability to adjust operating modes and dependence on power supply.
Features of heating a one-story and two-story building
For a one-story house, the most successful is the vertical layout, the main advantage of which is the ability to install pipes of equal diameter and high pressure values due to the difference in supply and return levels. When planning horizontal wiring and natural circulation, the slope of the line should be directed towards the boiler. It, in turn, allows you to create the optimal temperature regime and evenly distribute heat in the house.
For a two-story house, an increase in the efficiency of such a scheme is explained by enhanced circulation, which is possible due to an increase in the difference in the heights of the boiler and radiators of the second tier. Hot coolant enters the distribution tank on the second floor or the attic, and then goes to the heating devices along an inclined line. The organization of the system with natural circulation involves the installation of a supply pipe at an angle of 5 mm every 2 meters. The two-pipe heating system of a two-story house can be combined with a single-pipe.
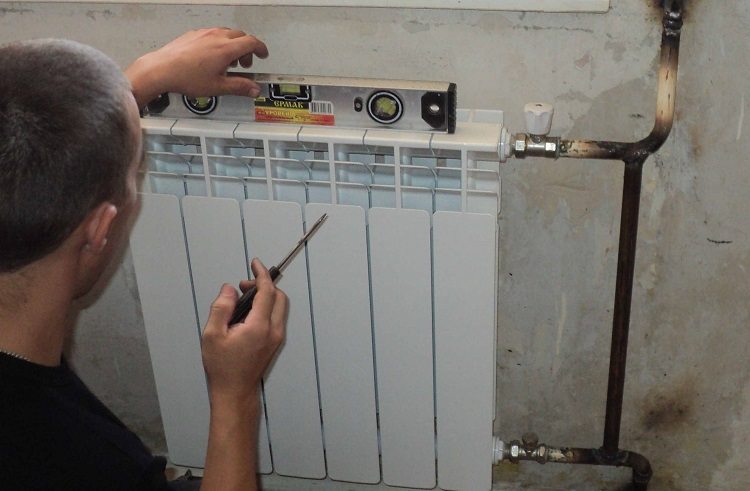

In order for the system with natural coolant circulation to function normally, the required level of pipe slope must be observed when installing the network
Pay attentionmane! The quality of heating in the house is associated with the circulation of the coolant, which depends on the diameter of the pipes used for wiring, their material, the number and radius of turns, the presence and type of shutoff valves.
The disadvantage of two-pipe heating using both natural and forced circulation is the high consumption of pipes. In this regard, it is worthwhile to decide in advance which pipes to use - polypropylene, metal-plastic or copper. The latter will cost more than the first two types.
Installation Rules
When installing a two-pipe heating system of a private house with your own hands, it is necessary to observe some technological rules. The circuit should consist of two pipes: the top with hot water and the bottom with chilled. The bias towards the last battery included in the system should be at least half a percent (better than 1%).
If the network has 2 wings, made mirror-like, then the final radiators must be installed at the same level.The lower trunk should be parallel and symmetrical to the upper. For maintenance and repair, radiators and process units are equipped with cranes. Preventing temperature loss during transportation of the coolant by wiring will help warm the supply pipe.
The sizes of valves, fittings and faucets must comply with the parameters of the pipes. Properly organized wiring eliminates overlaps, which are the cause of the formation of air jams, and angles of 90 degrees, which create resistance. Do-it-yourself fastening of the steel pipeline is carried out in increments of 1.2 meters.
The two-pipe heating system of a private house (multi-story or one-story building) is a closed loop, which allows you to effectively maintain the required temperature. Such a network can be started and installed by oneself, but for this it is desirable to have a project and specialized education.






