A few decades ago, it was almost impossible to imagine plastic pipes as the basis for a heating system. Now everything is made of polymeric materials: pipes for water supply systems, and for sewers, and for heating. PVC technical characteristics allow these products to be used in systems with extreme conditions, and in some respects they will even surpass the usual metal pipes.
Content
What plastic pipes can be used for heating?
Traditionally, polypropylene (mainly reinforced) pipes or metal-plastic (essentially the same plastic reinforced structures) were used for heating. PVC products usually went into the background.
Polyvinyl chloride pipes began to appear on public sale in the middle of the last century, and they were developed for use in the space industry. As for domestic use, initially products made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) were used only for laying water supply systems and pressureless sewage. Such a strict limitation was due to too low a temperature that this material could easily withstand: only 55-60 degrees.
Over time, the production of PVC products improved, and a new modification of products made from this material appeared on the market - PVC pipes with the addition of chlorine. The technical characteristics of chlorinated PVC significantly exceed those of ordinary polyvinyl chloride, so this modification can be easily used for hot water supply and for heating. The new PVC got its designation - CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride).
PVC plastic pipes for heating: advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of modern plastic pipes:
1. Easy to install. Thanks to the use of adhesive bonding technology, the time resources needed to create a high-quality, properly functioning heating system are reduced. When gluing the elements of the pipeline, mutual diffusion occurs between the plastic pipes and the fitting, so this type of connection will be close to monolith in strength.
2. Low probability of the development of bacteria and microorganisms inside the pipe. Due to the presence of chlorine in the composition, the material gains bactericidal properties. Products with a high susceptibility to the appearance of fungi include pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene and polypropylene.
It is interesting! The antibacterial properties of the CPVC material allowed this material to go beyond the scope of heating and water supply systems. Medical vessels are produced from CPVC for the collection and storage of donated blood.
3. The threshold of the working pressure optimal for the operation of the PVC pipe for heating is quite high: pipes with indicators PN16 and higher can be found on sale.
4. The fire safety of the PVC material makes the plastic pipe completely safe in everyday life. Polyvinyl chloride does not ignite, it dies on its own, as soon as the source of open flame disappears.
The disadvantages of the CPVC material are the following factors:
1. The presence of chlorine in the composition is a moot point. Chlorine is often used in water purification systems, but more and more information is emerging every year about its dangers. However, it is believed that the dose of chlorine that can enter the human body when drinking water from a CPVC pipeline is too small to cause any harm.
2. Due to the high stiffness of the material, some installation restrictions appear. This problem is solved by a large number of transition elements and competent design of the heating circuit.
Chlorinated PVC is not as cheap as regular polyvinyl chloride. The cost of arranging the wiring will be comparable to the heating of galvanized steel pipes. A factor that reduces the cost of using plastic structures is their low weight - reduced transportation and installation costs.
Specifications of PVC plastic pipes for heating
Among the chlorinated PVC pipes there are also varieties:
Green Line Type One. This material is able to withstand temperatures up to +80 degrees, but is actually intended for use in low temperature conditions. Such PVC pipes are necessary for the operation of air conditioning systems, cooling and freezing systems.
Deformation of this type of material begins at a temperature of +95 degrees. Its use is possible in heating systems and hot water supply, but only on condition that the operating temperature does not go beyond the limit.
Flow Guard Gold Type Two. More versatile and durable material that can withstand temperatures up to +100 degrees. It can be used in both internal and external networks. Of these plastic pipes, even risers can be mounted.
Comparison of the characteristics of the pipeline from ordinary PVC and CPVC are presented in the table.
Table 1
| Properties | Chlorinated PVC | Ordinary PVC |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 0,62 | 1,2-1,4 |
| Density (g / cm2) | 1,57 | 0,95 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W / Mk) | 0,14 | 0,22 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 50 to 55 | 18 to 26 |
| Design Strength (MPa) | 10 | 6,3 |
| Oxygen-permeability (upon reaching +70 in the system) | Less than 1 | 13 |
| Modulus of elasticity (MPa) | 2400 | 550 to 800 |
From the above table it can be understood that the only point at which CPVC indicators lose is a fairly low thermal conductivity. However, such characteristics can reduce heat loss in the heating system. This also means that the pipes themselves will not be very hot and condensation on them will be minimized. Thanks to this quality, the need for an additional thermal insulation system disappears.
Dimensions of plastic pipes for heating systems: how to choose the right one?
The dimensions (diameters and wall thickness) of pipes when designing a heating system is as important an issue as the choice of material for it. When determining the required dimensions, the following factors are taken into account:
- Selected heating wiring diagram;
- high-speed mode of movement of the coolant;
- diameter of the inlet and outlet of the boiler (if any);
- calculation of water cooling in a radiator;
- coefficient of resistance.
The standard calculation scheme is not suitable if the wiring in the house or apartment is complicated, or the system has mixed sources of heat (both radiators and underfloor heating). In this case, it is worthwhile to determine the required sizes with specialists, or rely on the successful experience in the construction of such systems.
Helpful advice! If you need to install a forced heating system, the best choice would be a pipe with the smallest possible cross section.With a reduced diameter of the plastic pipes, the flow rate of the coolant for heating is reduced, installation is simplified and the speed of movement of the coolant through the system is slowed.
It is worth remembering that when using too small diameters, the system will not be able to function correctly. There will be noises during the operation of heating, heat transfer will be ineffective. On average, a minimum pipe size is enough to heat a room with an area of 18-20 square meters.
The dimensions of PVC pipes for heating are presented in table No. 2.
table 2
| Diameter (mm) | Wall thickness (mm) | Rod Length (m) | Pressure |
| 16 | 1,2 | 5 | DN10-PN16 |
| 20 | 1,5 | 5 | DN15-PN16 |
| 25 | 1,9 | 5 | DN20-PN16 |
| 32 | 2,4 | 5 | DN25-PN16 |
| 40 | 3 | 5 | DN32-PN16 |
| 50 | 3,7 | 5 | DN40-PN16 |
| 63 | 4,7 | 5 | DN50-PN16 |
| 75 | 5,6 | 5 | DN65-PN16 |
| 90 | 6,7 | 5 | DN80-PN16 |
| 110 | 8,2 | 5 | DN100-PN16 |
| 160 | 7,7 | 5 | DN150-PN10 |
The dimensions shown may vary depending on the specifications of a particular manufacturer.
Installation of PVC plastic pipes for heating
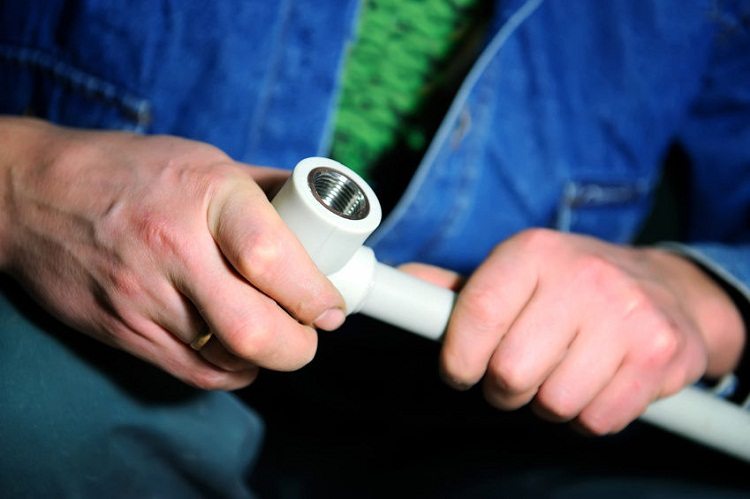
CPVC plastic pipes for heating are not suitable for soldering. A more reliable method is used to connect them - pipes made of chlorinated PVC are mounted using high molecular glue. This method has similarities with cold welding, since the special glue is similar in composition to the product material. Glue for pipes is the same CPVC, which is in a liquid state thanks to a diluent. The adhesive cures in a few minutes.
The assembly of the pipeline will consist of the following stages:
- drawing up an accurate diagram and marking the location of future structural elements;
- measuring, marking and cutting pipes into pieces of the desired length;
- selection of connecting and rotary elements: fittings, tees, angles;
- bonding all the elements in the right order;
- system strength test: water is launched under operating pressure. If insufficiently tight areas are found, gluing is repeated.
In addition to adhesive joints, a variant with threaded joints or fixation using loose flanges is possible.
Installation of heating systems made of chlorinated PVC is rational for economic and functional reasons. Due to the fact that this type of polymer is used relatively recently, it is difficult to say how much the PVC pipeline will serve practically. But the theoretical numbers are impressive - the life of polyvinyl chloride is called in the region of 50 years. This is significantly more than steel or cast iron structures under similar conditions.