It is quite simple to provide heat to a country estate or house according to the classical scheme of supplying the heat carrier from the boiler to the convectors. There are several options for wiring the supply lines and the branches for returning the spent liquid. In any of the options you can not do without laying heating pipes in a private house, and an accurate calculation will help to correctly design the system and save the project budget.
Content
Types of pipes for heating
The rational use of energy and the correct operation of the heating system in the house are not myths. Providing the simplest possible maintenance of heating equipment in a private building, the optimal cost of installing the system in a wooden house, and obtaining optimal efficiency with a minimum of costs are quite real. The main thing is to choose the right type of heating system, and lay all the pipes in the house so that the installation work is completed before the onset of the heating season.
The installation options for the heating system can be very different: from laying heating pipes in the floor screed, to outdoor installation directly on the internal walls of the premises, from laying communications under the floors in a wooden house or, using protective boxes and special foam covers directly in the ground.
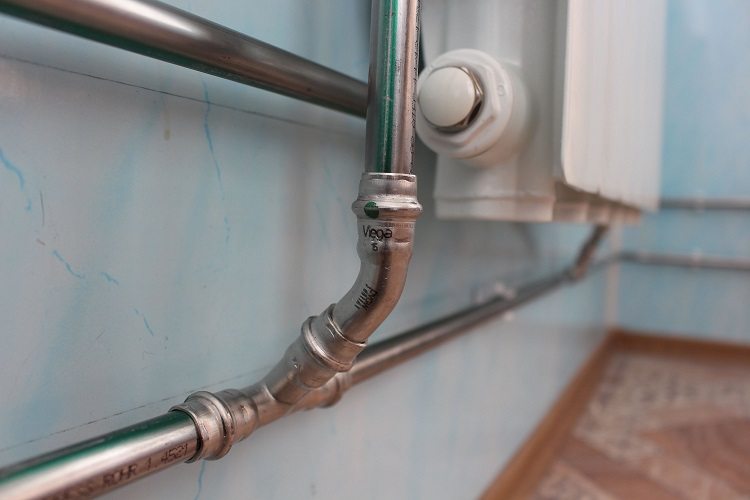
Different types of pipes can be used for heat transfer pipes of heating systems. The simplest option is metal pipes (steel, copper), suitable for laying in the ground in specially equipped concrete trays. More convenient to install, economical and no less reliable option is reinforced plastic pipes, with their help laying heating pipes in the floor is carried out. Polypropylene multilayer pipes with an oxygen barrier are used for “warm floor” systems; they are laid in a screed on a prepared surface.
Theoretically, everything is clear and understandable, but in practice there are a number of questions that need to be addressed: how to design a system for the implementation of autonomous heating, what kind of energy carrier to use so that the system is efficient and at the same time economical? And how to lay a heating pipe in a private house of an old building and at the same time maintain the uniqueness of the interior - to solve this problem, you need to think more than once.
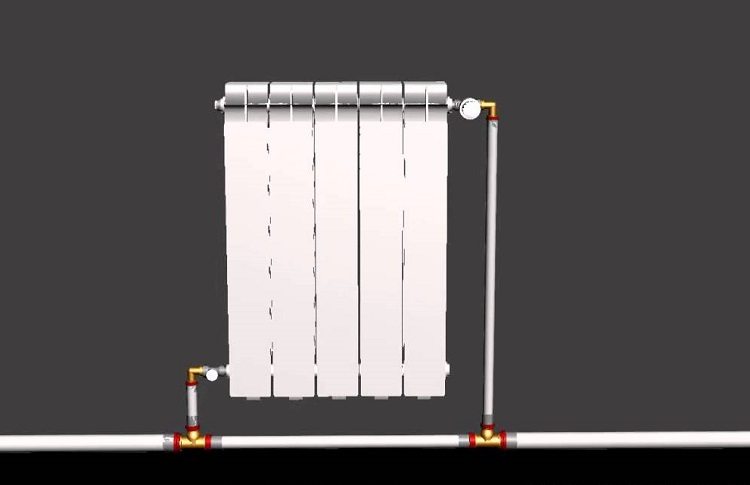
Important! To connect the hot water supply circuit from the boiler and connect the return branch of the system, exclusively metal pipes are used, the length of which must be at least half a meter.
Types of heating systems, installation features
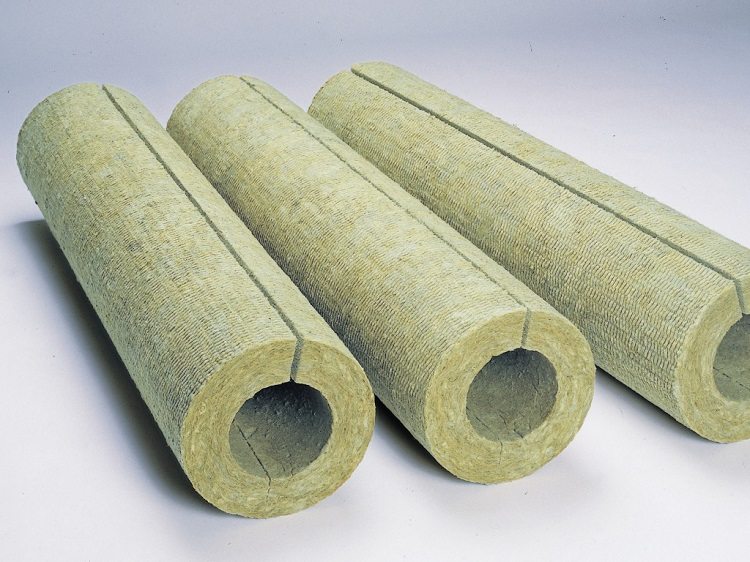
Installation work of the heating system in a country house or private building is carried out, as a rule, at the final stage of construction. By this time, the building is waiting for a cycle of finishing work, and in order to keep the heating circuit out of sight, pipes are laid, as a rule, in the floor screed. For basement floors, this is the best option, and heating pipes can be laid in a wooden house on the second floor and higher in the space between the walls of the premises, and they must use thermal insulation of each circuit of the heating system.
The danger is air, which is inevitably present in an open heating system. In order to avoid the formation of steam and a critical increase in pressure in the system, a so-called “expansion tank” is installed, the circuit is supplemented with an air pipe and Mayevsky taps at the top of the system, laying heating pipes of complex geometry is impossible without an air vent valve.
In systems with a top supply of coolant, the storage tank installed at the top of the system, most often in the attic, must be reliably protected from the cold, especially in the attic in a wooden house. Pipes laid in the ground are also complemented by a layer of thermal insulation.
Single pipe heating system
The heating circuit, implemented in the house on the principle of single-pipe wiring, is a system that sequentially transfers heat to the heating radiators. It is used in small buildings, in a wooden or brick house, in the event of a budget deficit allocated for the implementation of the heating system. Part of the circuit can be laid directly in the screed.
In the simplest embodiment, the single-tube system is not supplemented by additional adjustments on each heating radiator, and the coolant loses its temperature sequentially. Heated water (or other liquid used in the circulation circuit) comes to the finish heating radiator with a minimum temperature, pipes are laid in the screed using heat-insulating materials, or in the ground, protected by boxes made of foamed polymer.
Benefits:
- minimum pipelines;
- simple implementation;
- the possibility of natural circulation of the coolant;
- independence from the power supply network.
Disadvantages:
- there is no possibility of individual adjustment of radiators;
- the inevitable decrease in the temperature of the coolant as it passes through the heating circuit.
Having supplemented the single-circuit system with shut-off valves at the inputs and outputs of the radiators, and with a return flow circuit (bypass) at the input of each convector, we get a full-fledged “Leningrad” heating system.
Important! The inclusion in the pump circuit for forced circulation of the system increases the efficiency of the system. But without the electricity that is needed to operate the circulation pump, the efficiency of the system is significantly reduced.
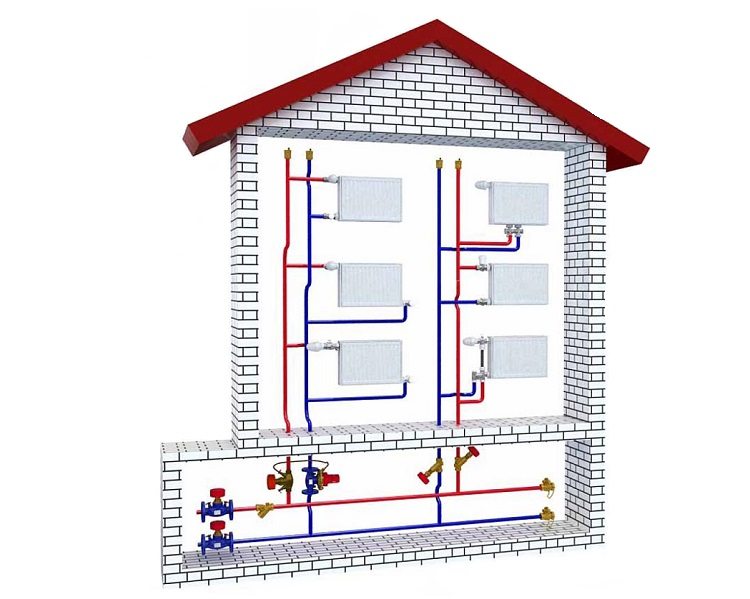
Two-pipe system wiring
The main advantage of this heating system is that each radiator is provided with its own system of direct and reverse supply of coolant. This opens up the possibility of precise individual temperature control in a private house. You can choose a comfortable temperature regime in any room, in a wooden structure this is especially important, and maintain the temperature of the coolant present in the main supply manifold. The disadvantage of the system is a large number of pipes. The laying of pipes of the external circuit in the ground is unacceptable without thermal protection of the pipes or above the freezing depth.
Heating system wiring options
Any type of heating system, whether it is a system with natural or forced circulation of a heat carrier, differs by the type of supply: a system with a vertical feed and a horizontal system.
In turn, vertical systems are divided into two subspecies:
- systems with a lower wiring, in which the supply main pipe passes along the floor of the first floor (or in the ground in the basement), from which vertical supply risers are realized;
- In a system with an upper wiring, the coolant is supplied, first of all, to the attic of the building (or under the ceiling of the upper floor, in a wooden house), passes through the main risers, then the spent liquid is returned to the heating boiler through the heating radiators.
In each case, the heating boiler is installed at the bottom of the system, on the basement or in the basement. The installation of the boiler directly on the ground is prohibited; the installation surface must be fire-safe, especially in a wooden house. Laying heating pipes in the ground is used if other installation options are not possible.
The horizontal system is divided into three subspecies, each of which works on the principle of forced circulation of the coolant.
The deadlock layout of the horizontal system wiring is implemented according to the principle of connecting the input of each radiator to a single supply system, the return of the waste coolant is also connected to the common circuit;
A system with associated circulation is characterized in that the coolant is supplied as in the first case, from a single system, and the waste fluid is withdrawn first to a collector common to all radiators, which is connected to the return path of the coolant circulation;
The best option is a manifold distribution scheme, where each branch of heat supply and removal is carried out through a common collector group, separate for a heated coolant, and for a cooled one. The laying of heating pipes is selected according to the best option.
The main advantage of our own heating system, implemented in a private building, is the ability to select the optimal temperature maintained in the house.
Sophisticated heat supply systems are characterized by a large number of control elements, allowing to maintain the required temperature in each individual room. In a small private building, simple systems with natural circulation of the coolant, due to the laws of thermodynamics and gravity, are most often used. The use of simple systems in a house is justified if the heated area of the premises is small and the overall construction budget is limited.