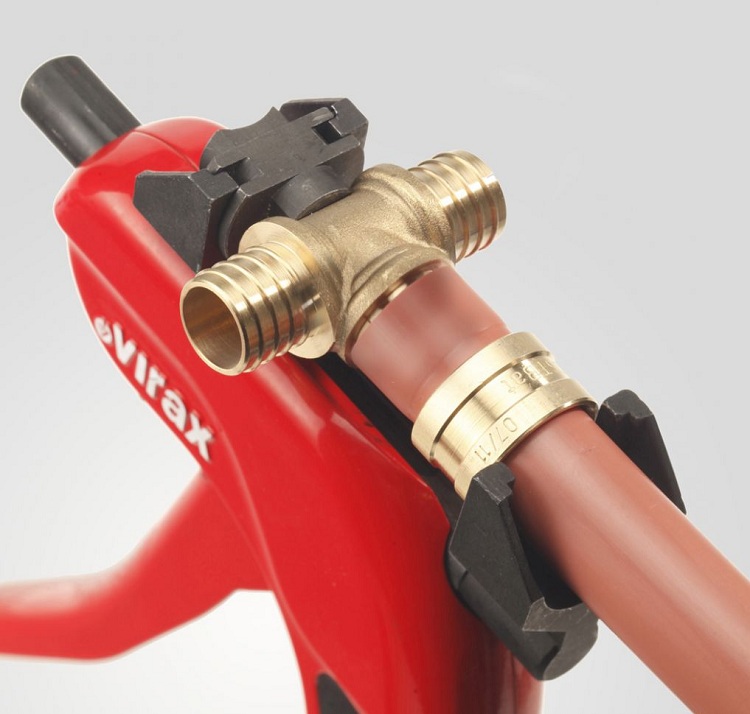
Pipe fittings made of cross-linked polyethylene are reliable assembly connecting structures installed using thread or welding. By fitting, the required tightness is achieved at the pipe joints. The type of fitting and the features of its installation are determined by the conditions in which the pipeline is laid, and by the general properties inherent in cross-linked polyethylene products.
When installing pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene, detachable or integral methods of connection are used
Content
Polyethylene pipes and fittings: features of the connection
The distribution of polyethylene pipes and the need to connect individual sections of the piping systems made up of them require consideration of the material:
- extremely ductile, which allows use without the use of threaded connections. However, the laying of certain types of pipelines without a threaded connection is simply impossible. For example, a well is drilled by screwing special fittings for HDPE pipes onto the thread, avoiding their thickening;
- retaining flexibility in the implementation of compounds at high temperature. Melting begins at a temperature of four hundred degrees, which allows seamless connection by welding;
- universal in breadth of areas of application and allowing installation work by non-specialists with the correct selection of the necessary tool and the diameter of the elements to be joined. For example, a single-layer pipe made of cross-linked polyethylene that can withstand heating to a temperature of ninety degrees Celsius provides cold water. For heating mains, multilayer-type products designed for use in the heating system will be needed, since they will cope with the coolant heated to 110º C.
Important! Fittings for PE pipes are selected taking into account both the diameter of the pipes and the method used to join them.
What are the ways to sew cross-linked polyethylene pipes
Cross-linked polyethylene pipe connections belong to two classes:
1. One-piece. They are divided into several types:
- press connections: axial, radial or self-tightening;
- welded butt.
- electrofusion.
2. Detachable.
- compression;
- threaded;
Pluggable PE fittings have come into mass use since their installation is carried out with amazing simplicity and does not require special skills and complex equipment. But the established elements need periodic monitoring and maintenance, pulling up weakened joints. Due to the inevitable violation of tightness over time, the installation of detachable joints with hidden installation is prohibited by building codes.
On the contrary, one-piece joints can be installed in inaccessible places and monopolized.Installation requires special equipment, its cost is much higher, but with proper work, the need for subsequent monitoring of installed fittings and maintenance is eliminated.
Preparation for installation
The execution of works on laying a pipeline made of cross-linked polyethylene requires compliance with several rules relating to the preliminary stage:
- selection of appropriate fittings;
- to ensure reliable operation of the system, it is desirable to dock at the outputs of the collector tees. The presence of turns on the tightness and strength will not affect, since the material is characterized by plasticity, it is easily bent;
- starting installation, the PE pipe is fixed using special brackets due to its high elasticity in order to maintain the desired shape;
- when laying water pipelines, measures are taken to protect against condensation during the supply of cold water and undesirable heat losses - during hot circulation;
- installation of heat-insulating gaskets and substrates is provided.
The minimum tools for installing PE pipes require the inclusion of:
- wrenches;
- secateurs or special hacksaw;
- manual or hydraulic press (for installing press fittings);
- expanders of the required diameters;
- a complete set of fittings.
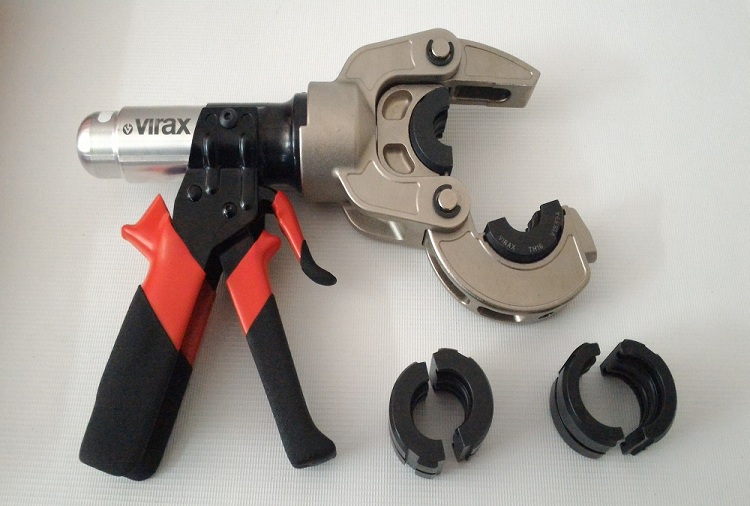

When choosing a press connection, you should take care of the availability of a special tool for installing such fittings
The presence of such a kit allows carrying out work of a sufficiently high level of complexity.
Features of the use of compression joints
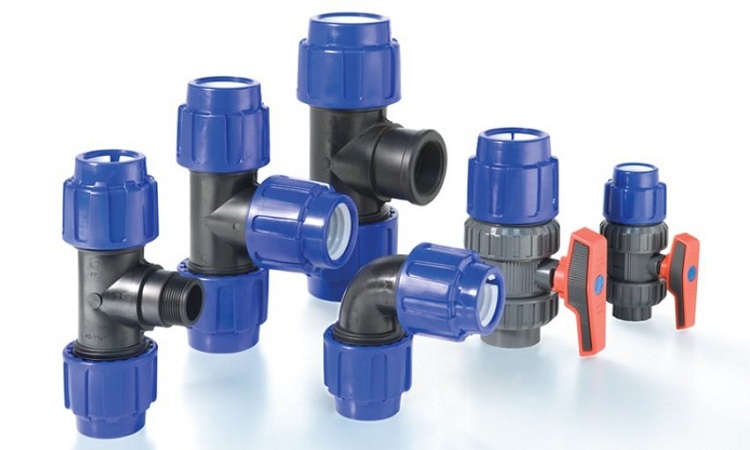
The use of collet connections is resorted to in cases where it is further planned to disassemble the structure, partially replace or connect new elements of the system. The compression fitting design consists of:
- housing;
- o-ring;
- compression (persistent) ring;
- collets (clamping ring);
- clamping nut.
The use of compression fittings is limited by the parameters of the working environment of pipelines:
- pressure up to sixteen atmospheres;
- temperature not higher than centigrade.
Therefore, they are used by:
- on water conduits of local importance;
- at the facilities of public utilities;
- in irrigation systems;
- in private households.
Installation of compression joints is carried out in the following order:
- At a right angle, the pipe is cut, burrs are eliminated and the edges are rounded. The length of pipe that will be inserted into the fitting is cleaned of contaminants.
- Putting a nut on the end of the pipe, set the clamping ring with a thickened part in the direction of the tail of the connected product.
- The product is completely inserted into the fitting, and the clamping ring is advanced by turning.
- The nut is first tightened by hand, the use of a wrench or special tool is used with caution so as not to twist.
Note! Access to compression joints must be maintained, since it is common for threaded nuts to unwind over time. In order to maintain the reliability of the joint, the nut must be tightened, therefore, it is advisable to avoid tightening the compression joints.
The use of fittings for butt welding of pipes
Butt welding, which is considered the most reliable method of connecting parts of the pipeline system, is used when working with large-diameter products. In this case, the use of fittings, direct and reduction:
- stubs;
- crosses;
- couplings;
- drives;
- tees;
- corners.
Welding is carried out using manual, mechanical or hydraulic units. Using a special soldering iron requires certain skills.If a hand-held device can be used successfully after not too long trainings, then a specialist is required to use more powerful equipment.
The joined elements in such cases are connected, with ensuring alignment, by centralizers. By machining the edges of the pipes with a trimming tool, they are given parallelism. Ensuring the accuracy of joining, the ends of the pipes are pressed against a two-sided heating element. The end of the pipe and coupling is heated to a temperature of 170º C, which ensures that the polyethylene is soft and supple. After that, the heating element is removed, the connected elements are pressed, manually, if a mechanical model is used and with the help of a hydraulic actuator - when connecting a hydraulic welding machine.
The connection is able to withstand operating pressures up to 12 MPa, and the use of sophisticated welding equipment virtually eliminates the appearance of marriage.
Electrofusion welding
The use of electrofusion welding requires a separate disposable fitting for each joint. Docking is carried out using a embedded heating element - a coupling with a built-in spiral:
- open;
- partially hidden;
- hidden.
The most common are fittings with a partially hidden spiral, combining optimal heating of a pipe made of cross-linked polyethylene and a coupling with a not too high cost.
Before welding, the outer surface of the pipe must be cleaned with conventional scrapers or mechanical devices from the oxide layer that impedes welding. The pipe is inserted into the fitting, to the terminals of which a voltage is applied. When heated, diffusion occurs, which contributes to the conversion of polyethylene of the connected elements into a homogeneous mass. Upon completion of cooling, the joint strength is such that the pipe is damaged during tensile tests.
Need to know! It is imperative that the joint remains motionless during the cooling of the joint. This is achieved by the use of positioners, fixing the connected elements until they obtain the necessary strength.
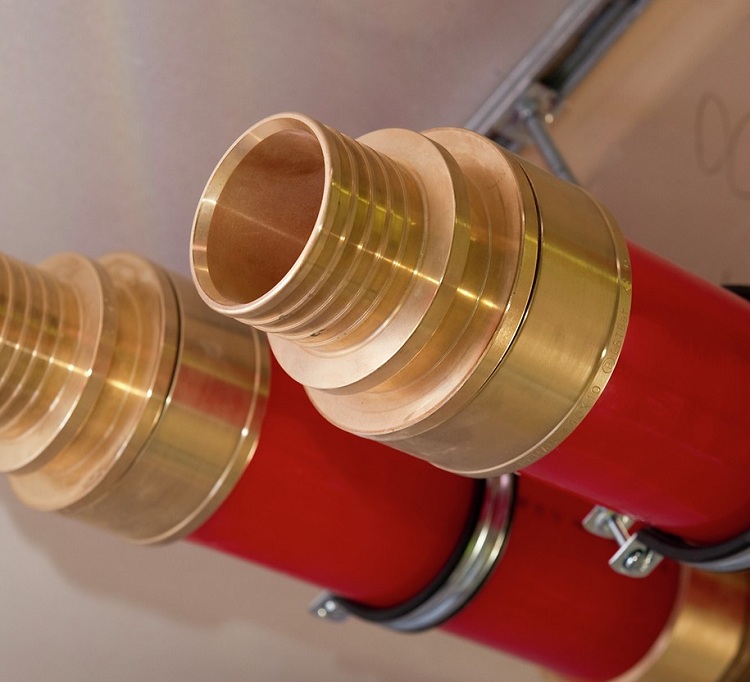
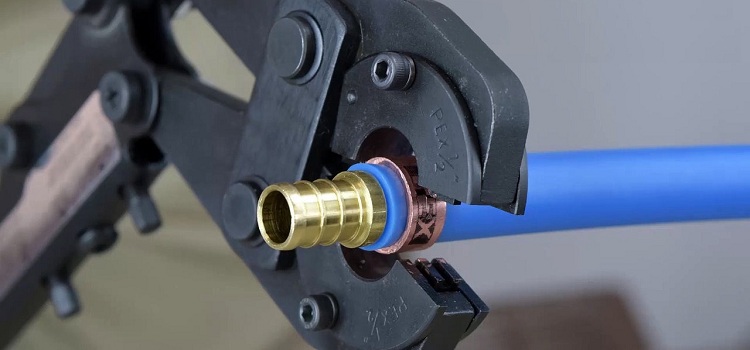
Fittings for press connections
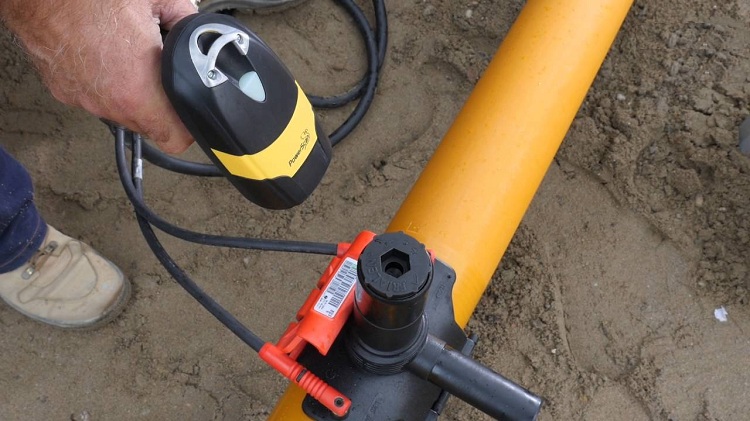
The integral connection of cross-linked polyethylene products is reliably ensured by press fittings. The design consists of a brass body and fitting, a steel sleeve and gaskets. Docking is carried out with a special tool that crimps and simultaneously deforms the fitting and pipe, thereby achieving their inseparability.
With a radial press connection use the tool:
- manual, with clamps of which a force is provided that is sufficient for crimping small diameter pipes;
- electrical (electromechanical, electro-hydraulic).
The versatility of the radial press tool allows you to successfully crimp a press fitting of any profile, provided that the right choice of interchangeable press pliers.
The axial press joint is based on the inherent material memory of cross-linked polyethylene, which tends to return to its original shape after deformation. Manual or electric tools work with products specially prepared for axial docking, installing brass and plastic fittings with slide sleeves.
The sleeve is put on the product and moves from its edge. The nozzle of the expander (expander) with closed segments is inserted into the pipe. The expandable segments turn the edge of the product into a funnel. Having taken out the expander, place the fitting of the fitting in the funnel. After that, the U-shaped jaws of the press tool capture both parts of the fitting, the sleeve pushes effortfully onto the end of the pipe, which is sandwiched between the sleeve and the fitting.After some time, the fitting is tightly enclosed by a pipe that preserves the memory of the material. The advantage of the axial press connection is the ability to save the bore of the pipes at the junction.
The use of self-clamping fittings is also based on the inherent cross-linked memory of the material. A sliding sleeve in self-locking joints replaces a polyethylene ring.
Having put on the pipe edge a ring of cross-linked polyethylene, an expander (expander) is inserted inside it and flaring is carried out. Upon the formation of a funnel, a fitting fitting is inserted into it. Within a few seconds, the memory effect of the material is triggered, the cross-linked polyethylene ring quickly returns to its previous shape, getting rid of deformation. The result is a tight pressing of the pipe to the fitting.
The advantage of a self-clamping fitting is that there is no need to use an axial press tool for connecting, dispensing with an adapted expander (expander) and tools for working with pipes.
A variety of fittings allows you to achieve a reliable connection of pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene, choosing in each case the optimal method of connection.











