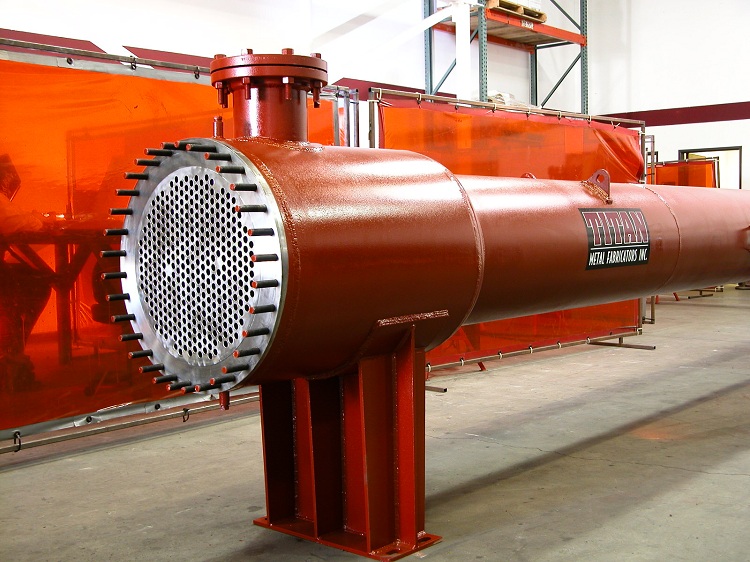
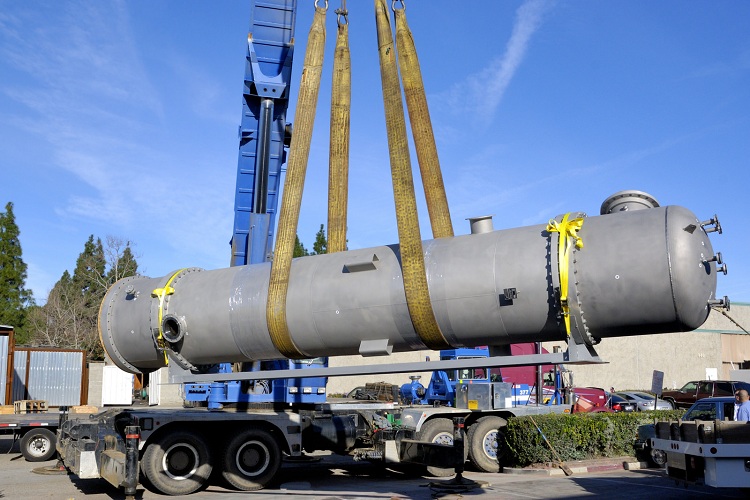
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger is a type of heat engineering devices and performs the function of transferring heat from the coolant to the heated substance. Depending on the specific case, the role of the coolant may be steam or liquid. To date, the shell-and-tube model of the heater has received the most widespread use.
Content
Areas of use
The production of these devices began in the early twentieth century. This was due to the fact that thermal stations needed large-surface heaters operating at high pressure.
Shell and tube heaters are used in many industries, including:
- Oil and gas industry;
- chemical production;
- food industry.
Almost every production is associated with the generation or absorption of heat, therefore, heat exchangers are in demand in various fields of human activity. The performance of equipment at enterprises, as well as the functioning of domestic air conditioners and heaters, cooling radiators in cars, etc., depends on their design and properties.
Note! Heaters of this type are most often used for cooling working fluids and heating the refrigerant for the operation of heat pumps.
Shell and tube heat exchangers are widely used as condensers as well as evaporators. Today, thanks to the development of industrial technologies, the design of heat exchangers has become more advanced and continues to be modernized.
Advantages and disadvantages of shell-and-tube heat exchangers
From a structural point of view, heat exchangers of this type are similar to the first models that were produced at the beginning of the twentieth century. The modernization of these devices affected only certain elements, however, the basis remained unchanged. Modern materials that are used for shell and tube heaters can improve their operational properties.
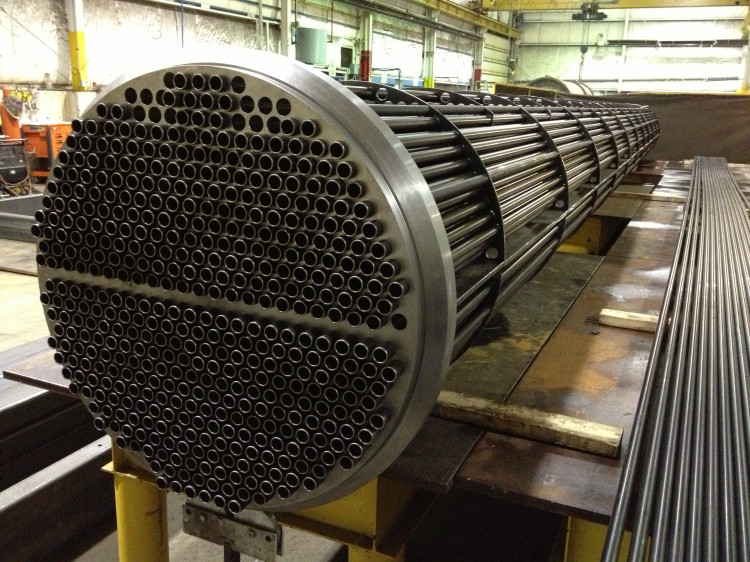

In the manufacture of heat exchangers, modern materials are used that significantly improve the quality of finished devices
Shell and tube heat exchangers are distinguished by a number of positive qualities, which allows them to remain indispensable elements of various industries to this day:
- resistance to water hammer in the system;
- the ability to work with polluted environments;
- low heat transfer rates;
- good performance;
- wear resistance;
- maintainability;
- resistance to high pressure;
- resistance to aggressive chemicals;
- operational safety;
- reliability and durability.
Heaters of this type have their drawbacks, including:
- quite large dimensions;
- high price.
The device and principle of operation
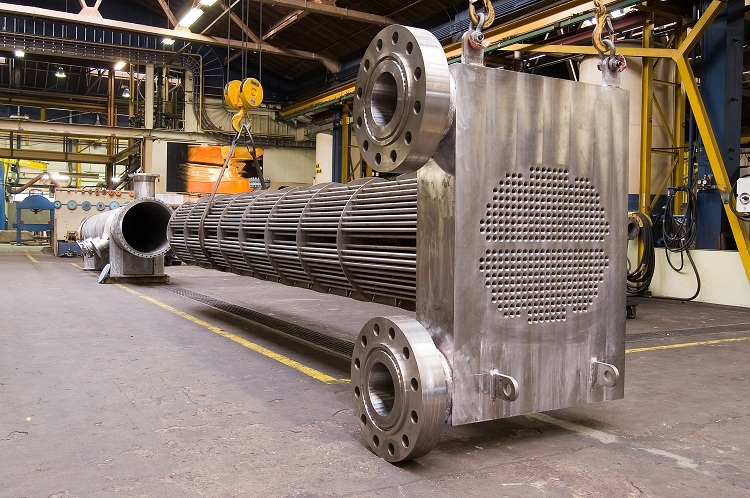
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger includes several structural elements. Consider the main ones:
- casing (housing);
- distribution and guide chambers;
- internal tube system;
- tube sheets;
- partitions and seals.
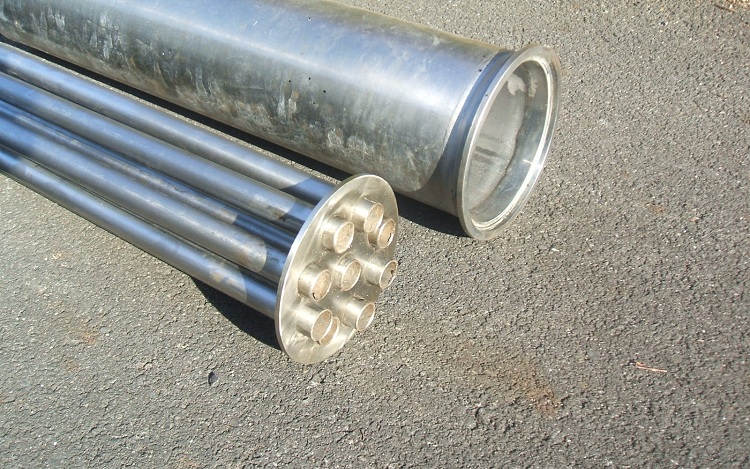

This device model is distinguished by the presence of a casing that hides the internal pipes, hence the name - “shell-and-tube”
Two nozzles are welded to the body. One of them is responsible for the supply of the working environment, and the other for the conclusion. Special flanges are welded to the ends of the casing.
In addition, the structure of such a heater includes tube sheets, between which pipes are welded, equipped with remote grids. This design forms the pipe system of the recuperator and allows the heater to be multi-pass.
Two nozzles are inserted into the bottom of the recuperator, which, in the same way as the nozzles of the casing, perform the supply and output functions. The bottom of the recuperator is equipped with flanges. Recuperator flanges are mating flanges of the housing. The pipe system of such a device is inserted into the housing. The grilles are fixed using special sealing elements and bolts between the flanges of the recuperator and the housing. This allows, if necessary, to seamlessly repair any element of the shell-and-tube device.
The principle of operation of this type of heater is as follows: hot and cold medium circulates through two different channels. The process of heat transfer is carried out between the walls of these channels.
Types of shell-and-tube heat exchangers
The shell-and-tube heater is quite complex, from a structural point of view, the apparatus and has several varieties that are worth paying attention to. Due to the design features (the presence of a recuperator), shell-and-tube devices are classified as a regenerative type.
In addition, depending on the direction of movement of the working media, shell-and-tube heaters are divided into the following types:
- direct-flow;
- crossflow;
- counterflow.
The shell-and-tube model got its name due to the fact that the pipes through which the coolant circulates are placed inside the casing. There is a dependence of the speed of the working medium on the number of tubes located in the casing. In turn, the higher the speed, the higher the heat transfer rate of the device.
Consider the basic materials from which such heaters are made:
- alloy steel;
- stainless steel;
- high strength steel.
Tubes of such devices can be made of the following materials:
- steel;
- copper;
- brass;
- titanium.
The use of such materials is due to the fact that heat exchangers are usually operated in harsh conditions and come into contact with aggressive substances that can cause corrosion.
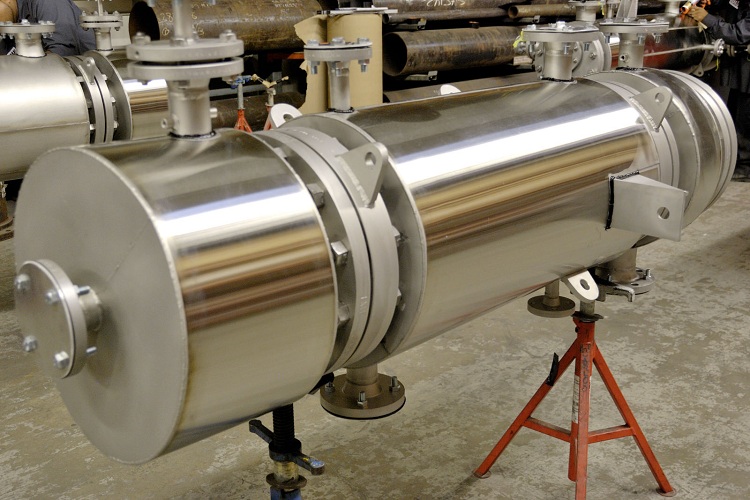

Heat exchangers are made from materials that have high corrosion resistance, such as titanium or stainless steel.
Important! Conventional steel is not suitable for a shell-and-tube heat exchanger because it has a low resistance to corrosion.
Shell-and-tube models are also divided into types. Today there are 4 types of these devices:
- a heater equipped with a temperature case compensator;
- heater with static (fixed) tubes;
- device with U-shaped and W-shaped tubes;
- floating head device.
Shell-and-tube heaters can be located in space horizontally, vertically or at a certain angle.
Heat transfer coefficient increase
Industry does not stand still - constantly upgrading heat exchangers. Improvement of technical characteristics is achieved through the use of the following methods:
- creation of turbulent flows;
- the implementation of spiral inserts, due to which a longitudinal and transverse flow around the tubes is formed;
- production of profile and twisted pipes;
- the use of mixtures, which include liquids and gases;
- creating vibration of surfaces that are responsible for heat transfer;
- pulsating flow of the working environment.
The above methods can increase the heat transfer coefficient. It is also common to use several methods at once. Such a combination can significantly increase the operational characteristics of a shell-and-tube heater by a factor of 2–3. It is also worth noting that some methods not only increase heat transfer rates, but can also perform other useful functions. For example, turbulent flows prevent the formation of salt deposits on the inner walls of the pipes, which eliminates the narrowing of the lumen of the tubes.
Continuous improvement of the design of the heat exchanger allows to increase heat transfer and increase operational characteristics
Heat exchanger selection tips
The shell-and-tube heater calculation program needs a clear statement of the initial data. A good recuperative device requires a well-defined circuit. There are several points to consider when choosing a shell and tube heat exchanger. These provisions are very important for calculations.
First of all, it is worth noting that for liquid and gaseous coolants there is a specific circulation speed through the tubes. As mentioned above, the higher the speed, the better heat transfer, respectively. For liquid media, the speed ranges from 0.6 to 6 m / s. For gaseous media, the speed can be from 3 to 30 m / s. However, the amount of energy expended also depends on the speed, therefore, in some cases, the coolant speed is underestimated to reduce electricity consumption.
When choosing tubes, you should pay attention to the material of which they are made, as well as their diameter. The material of the tubes is selected depending on the working medium that will circulate through them. It must be remembered - the more aggressive the environment, the more reliable the tube material should be.
Important! If the system will be cleaned using acid, then it is recommended that you choose stainless steel tubing. The stainless steel is characterized by high anti-corrosion properties, has excellent resistance to aggressive reagents and, in addition, has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are rather bulky devices, therefore, when choosing them, it is worth considering their sizes, so that in the future there will be no difficulties with their transportation and installation.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that after installation work, there must be enough space in front of the recuperator in order to carry out operational repairs of the device if necessary. There should be enough space so that the pipe system can be removed from the housing. The shell-and-tube heat exchanger must have a design that takes into account free access not only to the main elements, but also to other spare parts. This is especially true of control devices.
Tube and Shell Heat Exchanger Operation Tips
Heat exchangers of this type, although they are quite unpretentious devices, however, and sooner or later they need preventive cleaning or repair.
Repair of the heat exchanger entails some consequences - most often this is a decrease in the heat transfer coefficient. The most vulnerable part of the shell and tube heater is the tube. As a rule, it is they who cause the breakdown. Knowing about this feature of heat exchangers, experts advise to purchase them with a margin. In addition, problems often arise when these devices are regulated by condensate. Any changes entail deviations in the heat transfer area. Changes in heat transfer area are usually non-linear.
Doing such a device with your own hands is quite difficult, and in some cases impossible. The shell-and-tube heat exchanger is a very complex equipment, the production of which requires strict adherence to the technological process, which includes many stages.








